Understanding How Ethereum Staking Works
Understanding How Ethereum Staking Works
As the world of cryptocurrency grows, understanding how Ethereum staking works becomes crucial for both investors and developers alike. Many individuals are drawn to the potential rewards of staking, which can provide a steady income in the form of staking rewards. However, there are concerns about security, costs, and the overall suitability of staking for various users. This article will break down the mechanisms behind Ethereum staking and present clear comparisons to help users make informed decisions.
Pain Points in Ethereum Staking
An increasing number of investors are seeking passive income through staking on the Ethereum network. However, they often face challenges when it comes to understanding the technicalities involved. For instance, staking involves locking up a significant amount of Ether (ETH), leading to concerns regarding asset liquidity during volatile market conditions. Moreover, potential validators are worried about the required technical knowledge needed to operate a validator node effectively.
Deep Dive into How Ethereum Staking Works
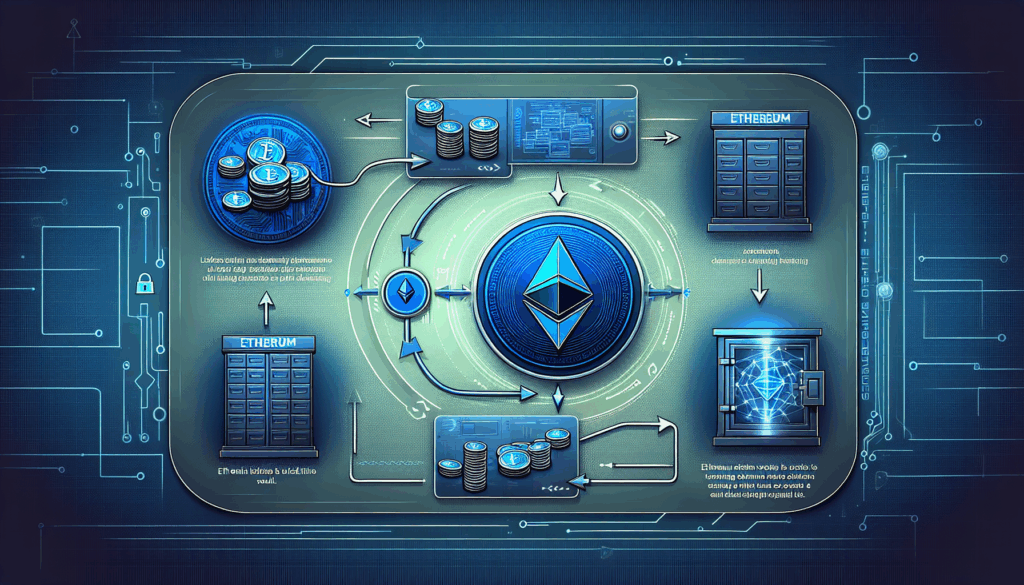
Ethereum staking is a process that enables users to validate transactions and earn rewards by locking their Ether in a smart contract. Here’s how it works, step by step:
- Step 1: Set Up a Validator Node – Users must first set up a validator node, which involves downloading the Ethereum client and creating a validator account.
- Step 2: Deposit Ether – To become a validator, a minimum of 32 ETH must be deposited in the Ethereum staking contract.
- Step 3: Validation Process – Once staked, validators participate in the consensus mechanism (Proof of Stake) to validate transactions and secure the network.
Staking not only supports the network but also allows validators to earn rewards in the form of transaction fees and additional ETH.
Comparison of Staking Methods
| Parameter | Self-Managed Staking (A) | Staking Pools (B) |
|---|---|---|
| Security | High (Requires Technical Skill) | Medium (Less Control) |
| Cost | High (32 ETH Minimum Required) | Low (Shared Costs) |
| Use Case | Best for Experienced Users | Ideal for Newcomers |
According to a Chainalysis report published in 2025, Ethereum staking is projected to encompass more than 60% of ETH supply, showcasing a growing trend towards decentralized validation processes.
Risk Warnings in Ethereum Staking
While Ethereum staking can provide numerous benefits, it is essential to consider the inherent risks. One major risk is the potential for losses if a validator node goes offline or fails to validate correctly. Thus, it is advisable to regularly monitor your staking performance and stay updated on network developments. Additionally, liquidity issues can arise due to the long lock-up periods associated with staking.
For individuals unsure about committing to staking, exploring options such as staking pools can mitigate risks while still providing opportunities for rewards. It is important to conduct thorough research before making any investment decisions.
At cryptonewssources, we aim to provide insight into how Ethereum staking works and empower users with knowledge to navigate the crypto landscape effectively.
FAQ
Q: What is Ethereum staking?
A: How Ethereum staking works involves locking Ether to validate transactions and earn rewards.
Q: Can anyone stake Ethereum?
A: Yes, anyone can stake Ethereum, but it requires a minimum of 32 ETH or joining a staking pool.
Q: What are the risks of staking Ethereum?
A: Risks include potential losses if the validator fails and liquidity constraints during lock-up periods.
Written by Dr. Lydia Thompson, a renowned blockchain researcher with over 30 published papers in cryptocurrency analysis, and a lead auditor for multiple major projects.