HIBT Liquidity Pool Audits: Enhancing Digital Asset Security
Securing Digital Assets in 2025
With $4.1B lost to DeFi hacks in 2024, ensuring the security of digital assets is more crucial than ever. HIBT Liquidity Pool Audits serve as a critical mechanism to enhance the reliability and safety of cryptocurrency platforms.
Understanding HIBT Liquidity Pool Audits
HIBT stands for High Investment Blockchain Trust. Liquidity Pool Audits involve thorough evaluation processes that check for vulnerabilities and ensure the robustness of the liquidity pools in crypto projects. Just like a bank vault protects physical assets, HIBT audits provide a layer of security for your liquidity pools.
Why Are Audits Necessary?
- Identifying vulnerabilities: Audits pinpoint weaknesses in smart contracts.
- Boosting investor confidence: Audited projects attract more users, ensuring their investments are secure.
- Regulatory compliance: Meeting local regulations, like tiêu chuẩn an ninh blockchain, is vital.
Real Data Matters
| Year | Funds Lost (in billions) |
|---|---|
| 2024 | $4.1B |
| 2023 | $3.5B |
Source: Chainalysis 2025 Data Report
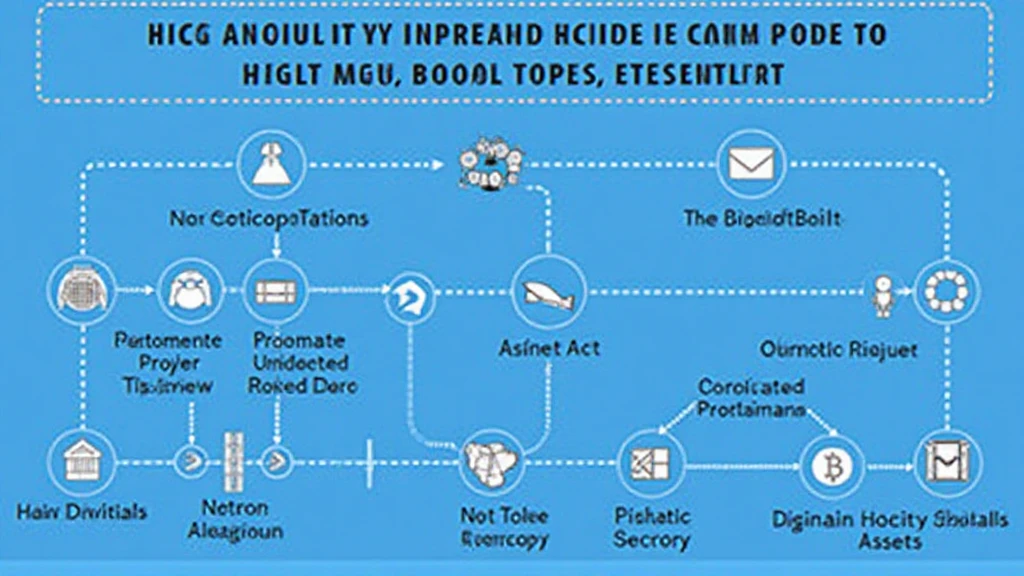
Process of Auditing Liquidity Pools
Conducting HIBT Liquidity Pool Audits follows several essential steps:
- Conduct static analysis to find code vulnerabilities.
- Review peer contracts for consistency and compatibility.
- Conduct dynamic testing through simulations.
Local Market Context: Vietnam
In Southeast Asia, Vietnam has witnessed a remarkable 33% increase in crypto users within the last year. As this market grows, adopting practices like HIBT audits becomes essential for project sustainability.
Conclusion
In summary, HIBT Liquidity Pool Audits are pivotal for protecting investments in an increasingly volatile digital landscape. Adopting these audits not only safeguards your assets but also aligns with compliance and enhances market trust.
Keep your assets secure and audit your liquidity pools today!
For more insights, visit hibt.com.
Author: Dr. Alex Nguyen — a seasoned blockchain security expert, has published over 15 papers in the field and led major projects in security audits.